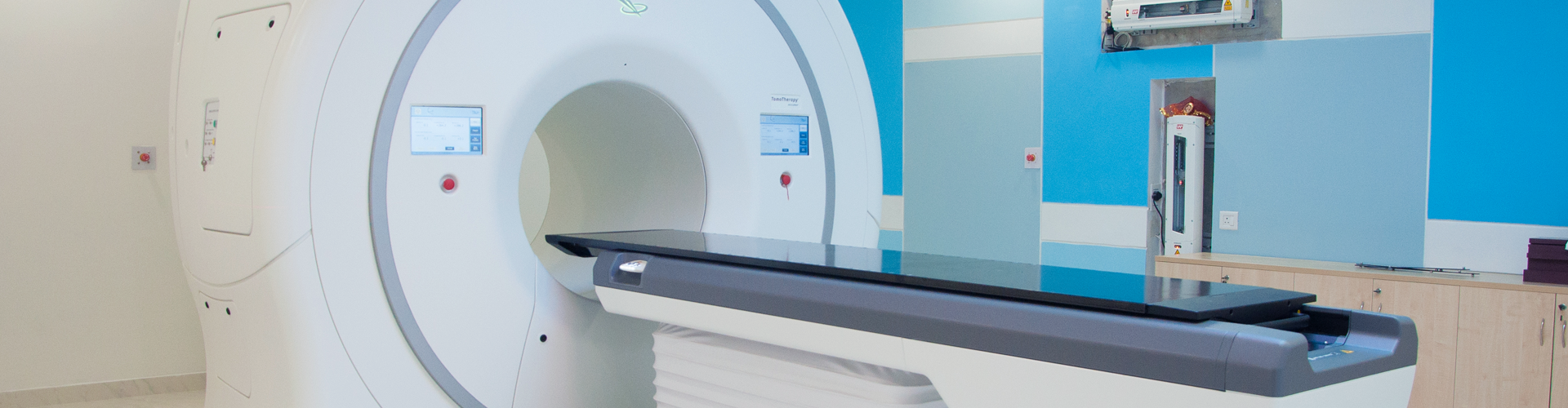
Tomotherapy is a form of intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT), in which the radiation is transported slice-by-slice. The word Tomotherapy has emerged from a Greek prefix - tomo, which means sl.....
Tomotherapy is a form of intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT), in which the radiation is transported slice-by-slice. The word Tomotherapy has emerged from a Greek prefix - tomo, which means slice. Tomotherapy is an advanced technology by which powerful and precise radiation beams are continuously produced to treat inoperable tumours. The inbuilt CT scanning helps in confirming the size and position of the tumour prior the treatment.
Cancer patients who have reached the extreme level to dose are suggested to undergo this therapy.
-
To decrease the symptoms of cancer in advance, or in the later stages.
-
As a primary treatment to cancer.
Preparing for Tomotherapy
- Before the treatment, the doctors use 3D images from the combination of scanning technologies such as MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) and CT (Computed Tomography) scans to establish the precise contours. Special software is used for each treatment volume and any regions of risk.
- To match the doctor’s prescription as closely as possible, the therapy technology calculates the appropriate patterns, position, and intensity of the radiation beam to be distributed.
- The patient will be asked to change into a loose-fitting gown provided by the Medanta.
During the treatment
- During the procedure, the patient is made to lie down on the table which can move in all four directions. The area which is not to be exposed to the radiations will be covered by a material.
- The machine directs the radiations on the area to be treated. The radiographer operates the machine and the patient can talk to him/her via intercom.
- The procedure requires the patient to remain as still as possible. It takes only a few minutes each day and is completely pain-free. In the first week of therapy and for the coming weeks, the staff and oncologist ensure that the therapy continues in synchronisation with the devised plan.
After the treatment
- During the weeks of treatment, the patient is monitored closely, for treatment schedule, doses and general health.
- The patient will undergo some imaging tests so that the doctor can figure out the efficiency of radiations.
- If the patient feels allergic to radiations or observes any side-effects, which happens rarely, the same should be conveyed to the doctor or the oncologist.

The advantages of Tomotherapy are:
- The technology generates detailed pictures and thus enhances the procedure for treatment.
- Tumour cells can be easily identified through using the computerised imaging system.
- Tomotherapy is a more flexible treatment to target multiple, complex, and sensitive areas in the brain.
- The technology can significantly improve the diagnosis.
- The procedure also limits unnecessary medical treatments.

The risks associated with Tomotherapy are:
- Skin problems such as irritation and rashes, difficulty in eating and loss of appetite, dry eyes, throat, and mouth.
- Nausea and headache.
- Changes in the urinary and bladder systems.

The limitations of this therapy are:
The radiation can damage the surrounding healthy tissues.
There are some benefits of tomotherapy, which gives the patients a sense of relief. But, those benefits come with some risks too, which are mentioned below:
-
The treatment is very precise. Less time consuming. When eliminating the tumour is not possible, it is used as a palliative treatment. Quick recovery. No requirement of anaesthesia. Painless procedure.

-
Diarrhoea. Swelling in the leg. Bladder issues. Skin Problems. Dry Mouth. Vomiting. Difficulty in urination.

-
Steps to be taken before Tomotherapy You will be asked to follow specific diet prior to the procedure. You may also be advised to stop or avoid certain medication. Our team of doctors will guide you through the process and will make sure you stay stress-free during the procedure.

-
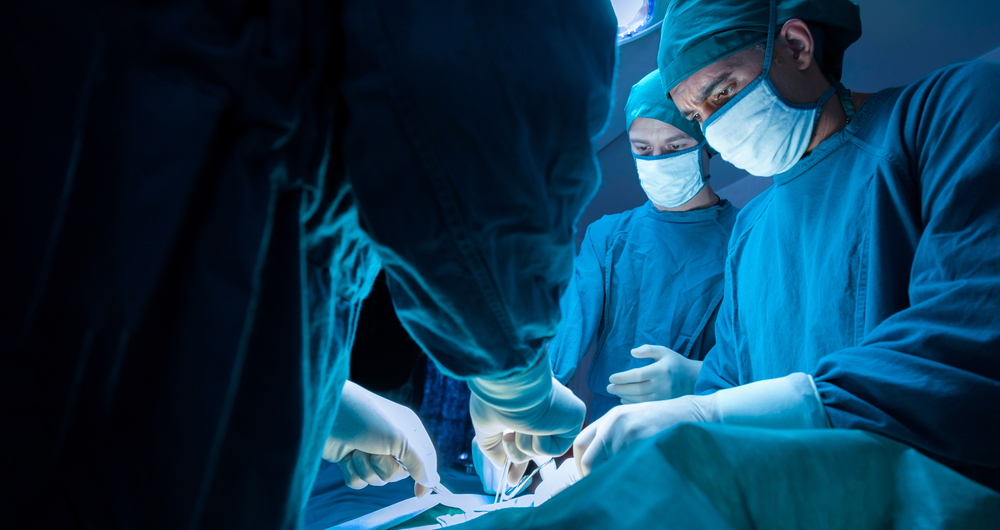
What happens during the procedure? The surgery starts with the scanning of the treatment area using 3D imaging. It is very important to have accurate clinical measurements so that damage to normal cells is minimal. A thin beam of radiation is made to rotate around the body and enter from different directions to kill the tumour cells. A computer processor will monitor the delivery of radiation rays at the pre-determined intensity, at any given point of time.
-
After Tomotherapy Your doctor at Medanta will provide you with all the post-procedure instructions. You may need extra rest while your tissues heal and regenerate. Be gentle with your skin in the treatment area as it takes time to heal. You might have to visit your doctor a few times post therapy to monitor the results of the therapy.
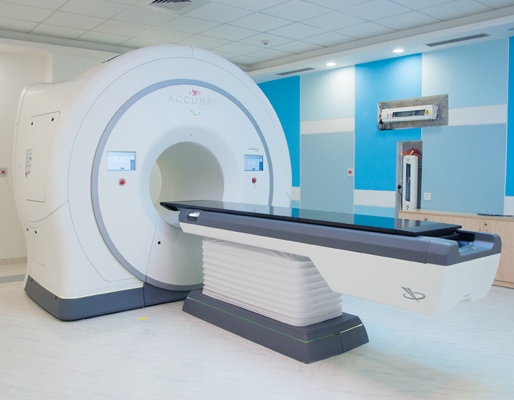
• The unique 4D kV imaging feature provides 4D volume images of the tumours that are moving. The radiologists can target them precisely without harming the healthy tissues present in the proximity.
• The technology offers non-invasive, internal immobilization of anatomies that are affected by the motion of the body due to respiration via comfortable and simple breath holding techniques.
Intrafraction monitoring continuously updates the affected part which is then targeted by the radiation beams. The beam shaping is performed with the advanced multi-leaf collimator which renders precision and accuracy in the procedure of targeting.