Essential Things and Reality of Gallstone Treatment
Gallstone Overview
When digestive fluid hardens up inside the gallbladder, it turns into gallstones. The gallbladder stores digestive fluid (bile) and is positioned beneath the liver, on the right of the abdomen. It is a small-size organ with the shape of a pear.
A gallstone may be of any size. Its size may either resemble that of a golf ball or a sand grain. There can be either a single gallstone or multiple gallstones in the gallbladder of an individual.
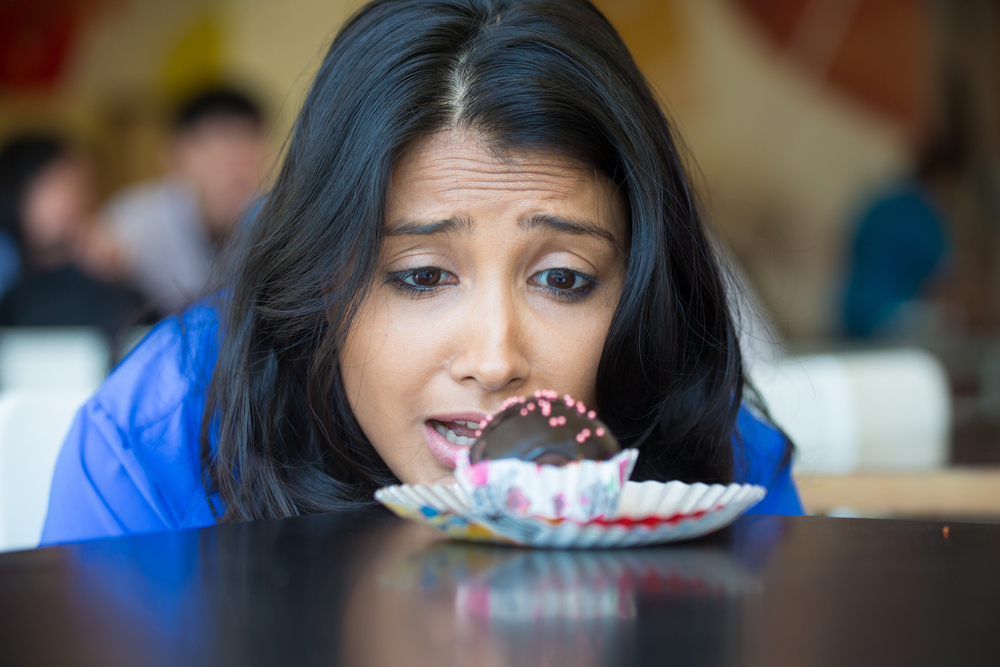
The symptoms of gallstones vary from one individual to the next. In some cases, gallstones are accompanied by certain symptoms. On the other hand, some individuals may be asymptomatic usually. Asymptomatic gallstones do not require any surgery, but gallbladder surgery is necessary if gallstones start showing symptoms.
Gallstone Causes
While many studies have been conducted on gallstones, their causes are still unclear. Most health care professionals and experts believe certain factors may trigger them in individuals. These include the following:
- Excessive cholesterol in bile: Bile absorbs cholesterol released by the liver. Generally, the former dissolves the cholesterol that comes from the latter. When the liver excretes more cholesterol than the capacity of bile to dissolve it, additional cholesterol develops into crystals. These crystals turn into gallstones in the subsequent stages.
- A high level of bilirubin in the bile: Gallstones may also form in the gallbladder due to a higher level of bilirubin. The liver releases this chemical after the breaking down of red blood cells by the body. Due to certain conditions, the liver may produce more bilirubin than it generally does. This excessive bilirubin in bile leads to the formation of gallstones.
- Improper emptying of the gallbladder: Total emptying of the gallbladder is necessary for the health and well-being of an individual. If it doesn’t happen, bile gets concentrated, which may cause gallstones to form in the gallbladder.
Types of Gallstones
Depending on the method of formation due to excessive cholesterol or bilirubin, gallstones can be put under the following two categories:
- Cholesterol gallstones: These gallstones are formed due to excess, undissolved cholesterol and are yellow.
- Pigment gallstones: These gallstones are black or brown and are formed due to excessive bilirubin.
Gallbladder – Symptoms
The symptoms of gallstones include the following:
- Intense pain in the top right or central part of the abdomen that happens all of a sudden
- Pain in the shoulder blades, which often seems to be a back pain,
- Pain on the right side of the shoulder
- Vomiting or nausea
Gallstone Complications
A gallstone, following its formation, may show up the following complications:
- An inflamed gallbladder - Cholecystitis
- Bile duct blockage – Choledocholithiasis +/-
- Pancreatitis duct blockage
- Gallbladder cancer
When Should You See a Doctor?
Consider seeing a doctor if you experience the following:
- Bloating, indigestion, gases in abdomen
- Intense abdominal pain that doesn’t go away easily
- Yellowing of the skin
- Chills with a high fever
Gallstone Prevention
Gallbladder surgery is not necessary for an individual unless they develop symptoms due to the formation of gallstones. One of the best ways to eliminate the need for the operation of the gallbladder is to adopt preventive measures.
"Prevention is better than cure," as the saying goes. Some effective measures for preventing the formation of gallstones include the following:
- Taking meals at the right times each day.
- Shedding excessive fat in the body slowly to lose body weight.
- Adding fibre-rich foods or items to the diet.
- Maintaining the right body weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet.
Gallstone Treatment
The treatment plan for gallstones depends on their diagnosis which is done based on the complications. The following tests and methods are used for diagnosing a gallstone in an individual:
- Abdominal ultrasound
- Endoscopic ultrasound
- Imaging tests like HIDA scan, CT scan, MRCP, and ERCP
- Blood tests for pancreatitis, jaundice, infection, and other complications
Most cases of gallstones do not necessitate treatment. However, you need to see a doctor if you experience acute pain in the abdomen and other symptoms. Depending on the diagnosis of gallstones in your gallbladder of your body, a doctor may suggest the following treatment options for you:
Observation – If asymptomatic gall stone disease
- Gallbladder surgery: Your doctor may suggest the removal of the gallbladder if they feel it is necessary to relieve you from the symptoms of gallstones. The removal of the gallbladder wouldn’t cause any problem and you can live with it. Following gallbladder surgery, the liver transports bile to the small intestine.
- Safe, day care procedure that can be done laproscopically (minimal invasively)